Sung Yul Lim, Yang-Rae Kim, Kyungyeon Ha, Jong-Kwon Lee, Jae Gyeong Lee, Woohyuk Jang, Jin-Young Lee, Je Hyun Bae, Taek Dong Chung*
Energy and Environmental Science 2015, 8(12), 3654−3662
Publication online: October 15, 2015
Publication date: December 1, 2015
DOI: 10.1039/c5ee02863a
ISSN: 1754-5692
Journal country: England
Publisher: ROYAL SOC CHEMISTRY
URL: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/ee/c5ee02863a
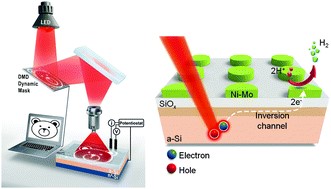
Abstract: Hydrogen is in the lime light as a carbon-free alternative energy source due to its high energy conversion efficiency. Solar-driven water splitting is one of the most promising methods for renewable hydrogen production. However, commercialization of a photoelectrochemical hydrogen production system remains a great challenge. One of the emerging concerns is the development of an inexpensive and transparent catalyst, which does not obstruct the light pathways to the semiconductor electrode. Here we report a non-noble metal electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution, Ni-Mo, which is directly patterned on amorphous Si (a-Si) by light-guided spatially selective electrodeposition without consecutive photolithography processes. A light pattern is illuminated onto the a-Si using a digital micromirror device to commence the photoelectrochemical deposition. The catalyst patterned by the proposed method not only admits sufficient light to a-Si but also enables long distance carrier transport along the inversion layer, as previously observed in crystalline Si (c-Si) photocathodes. This new electrodeposition method enables mask-free patterning on a-Si and is expected to expedite a lower cost, more efficient, and self-biasing integrated photoelectrochemical water-splitting device.
Download: 28_Energy and Environmental Science.pdf

 27. Impact of surface chemistry on nanoparticle-electrode int...
27. Impact of surface chemistry on nanoparticle-electrode int...




















