Donghoon Han, Yang-Rae Kim, Chung Mu Kang, Taek Dong Chung*
Analytical Chemistry 2014, 86(12), 5991−5998
Publication online: May 20, 2014
Publication date: June 17, 2014
DOI: 10.1021/ac501120y
ISSN: 0003-2700
Journal country: United States
Publisher: AMER CHEMICAL SOC
URL: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac501120y
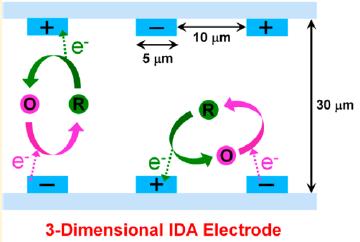
Abstract: We devised an electrochemical redox cycling based on three-dimensional interdigitated array (3D IDA) electrodes for signal amplification to enhance the sensitivity of chip-based immunosensors. The 3D IDA consists of two closely spaced parallel indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes that are positioned not only on the bottom but also the ceiling, facing each other along a microfluidic channel. We investigated the signal intensities from various geometric configurations: Open-2D IDA, Closed-2D IDA, and 3D IDA through electrochemical experiments and finite-element simulations. The 3D IDA among the four different systems exhibited the greatest signal amplification resulting from efficient redox cycling of electroactive species confined in the microchannel so that the faradaic current was augmented by a factor of ∼100. We exploited the enhanced sensitivity of the 3D IDA to build up a chronocoulometric immunosensing platform based on the sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) protocol. The mouse IgGs on the 3D IDA showed much lower detection limits than on the Closed-2D IDA. The detection limit for mouse IgG measured using the 3D IDA was ∼10 fg/mL, while it was ∼100 fg/mL for the Closed-2D IDA. Moreover, the proposed immunosensor system with the 3D IDA successfully worked for clinical analysis as shown by the sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I in human serum down to 100 fg/mL.
Download: 22_Analytical Chemistry.pdf

 23. Surface coverage and size effects on electrochemical oxid...
23. Surface coverage and size effects on electrochemical oxid...
 21. Tunable decoration of reduced graphene oxide with Au nano...
21. Tunable decoration of reduced graphene oxide with Au nano...

