Yang-Rae Kim, Hyo-Ju Seo, Jeong-Wook Oh, Hyunchang Lim, Tae Hyun Kim*, Hasuck Kim*
Electroanalysis 2013, 25(4), 1056−1063
Publication online: February 22, 2013
Publication date: April 1, 2013
DOI: 10.1002/elan.201200548
ISSN: 1040-0397
Journal country: Germany
Publisher: WILEY-V C H VERLAG GMBH
URL: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/elan.201200548/abstract
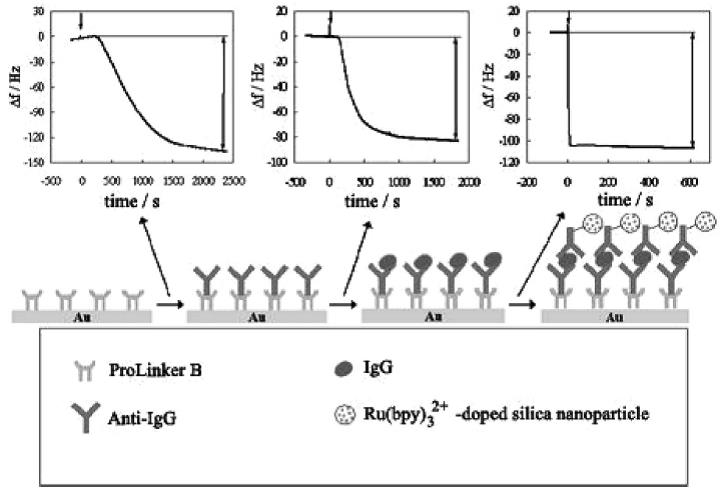
Abstract: An electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL)-based immunosensor for the detection of immunoglobulin G (IgG) has been fabricated using Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles and calix[4]crown-5 self-assembled monolayers (SAMs). Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles are prepared by the water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsion method. ProLinker B, a commercially available thiolated calix[4]crown-5 derivative, is utilized for the immobilization of anti-immunoglobulin G (Anti-IgG) on a gold electrode. The concentration of IgG is measured using a sandwich-type ECL immunosensor based on the proposed immunosensor. The ECL intensity is linearly proportional to the IgG concentration over the concentration range 5–30 µg mL−1. The detection limit of IgG is 1.5 µg mL−1.
Download: 17_Electroanalysis.pdf
 18. Enhanced electrochemical reactions of 1,4-benzoquinone at...
18. Enhanced electrochemical reactions of 1,4-benzoquinone at...
 16. Graphene-incorporated chitosan substrata for adhesion and...
16. Graphene-incorporated chitosan substrata for adhesion and...
















