Chung Mu Kang, Segyeong Joo, Je Hyun Bae, Yang-Rae Kim, Yongseong Kim, Taek Dong Chung*
Analytical Chemistry 2012, 84(2), 901−907
Publication online: December 13, 2011
Publication date: January 17, 2012
DOI: 10.1021/ac2016322
ISSN: 0003-2700
Journal country: United States
Publisher: AMER CHEMICAL SOC
URL: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac2016322
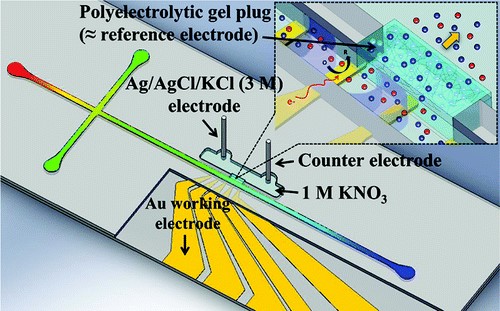
Abstract: We propose a new method for performing in-channel electrochemical detection under a high electric field using a polyelectrolytic gel salt bridge (PGSB) integrated in the middle of the electrophoretic separation channel. The finely tuned placement of a gold working electrode and the PGSB on an equipotential surface in the microchannel provided highly sensitive electrochemical detection without any deterioration in the separation efficiency or interference of the applied electric field. To assess the working principle, the open circuit potentials between gold working electrodes and the reference electrode at varying distances were measured in the microchannel under electrophoretic fields using an electrically isolated potentiostat. In addition, “in-channel” cyclic voltammetry confirmed the feasibility of electrochemical detection under various strengths of electric fields (∼400 V/cm). Effective separation on a microchip equipped with a PGSB under high electric fields was demonstrated for the electrochemical detection of biological compounds such as dopamine and catechol. The proposed “in-channel” electrochemical detection under a high electric field enables wider electrochemical detection applications in microchip electrophoresis.
Download: 13_Analytical Chemistry.pdf

 14. A BODIPY-functionalized bimetallic probe for sensitive an...
14. A BODIPY-functionalized bimetallic probe for sensitive an...
 12. Gold microshell tip for in situ electrochemical raman spe...
12. Gold microshell tip for in situ electrochemical raman spe...





















