Yang-Rae Kim, Sungyool Bong, Yeon-Joo Kang, Yongtak Yang, Rakesh Kumar Mahajan, Jong Seung Kim*, Hasuck Kim*
Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2010, 25(10), 2366−2369
Publication online: March 4, 2010
Publication date: June 15, 2010
DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.02.031
ISSN: 0956-5663
Journal country: Netherlands
Publisher: ELSEVIER ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566310001168
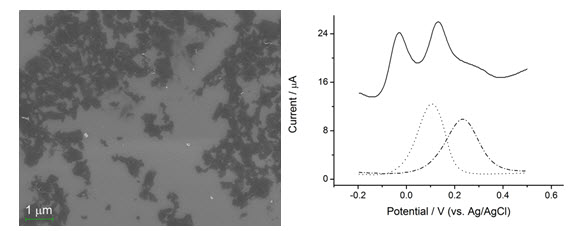
Abstract: Dopamine plays a significant role in the function of human metabolism. It is important to develop sensitive sensor for the determination of dopamine without the interference by ascorbic acid. This paper reports the synthesis of graphene using a modified Hummer's method and its application for the electrochemical detection of dopamine. Electrochemical measurements were performed at glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene via drop-casting method. Cyclic voltammogram of ferri/ferrocyanide redox couple at graphene modified electrode showed an increased current intensity compared with glassy carbon electrode and graphite modified electrode. The decrease of charge transfer resistance was also analyzed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The capacity of graphene modified electrode for selective detection of dopamine was confirmed in a sufficient amount of ascorbic acid (1 mM). The observed linear range for the determination of dopamine concentration was from 4 μM to 100 μM. The detection limit was estimated to be 2.64 μM.
Download: 6_Biosensors and Bioelectronics.pdf
 7. Enhanced electrogenerated chemiluminescence of a ruthenium...
7. Enhanced electrogenerated chemiluminescence of a ruthenium...
 5. Highly sensitive detection of DNA by electrogenerated chem...
5. Highly sensitive detection of DNA by electrogenerated chem...






