Se Won Bae, Jeong-Wook Oh, Ik-Soo Shin, Min Sun Cho, Yang-Rae Kim, Hasuck Kim*, Jong-In Hong*
Analyst 2010, 135(3), 603−607
Publication online: January 21, 2010
Publication date: March 1, 2010
DOI: 10.1039/b920998k
ISSN: 0003-2654
Journal country: England
Publisher: ROYAL SOC CHEMISTRY
URL: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2010/AN/B920998K?page=search
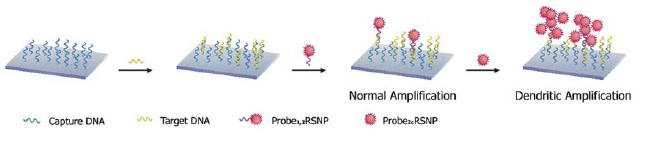
Abstract: This study describes the development and characterization of a novel dendritic signal amplification strategy. It relies on the use of two different Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles (Probe1,2RSNP and Probe2cRSNP) coated with complementary DNAs, which can be simply and conveniently self-assembled to build sandwich-type dendritic architectures on a gold grid. The performance of this dendritic amplification route was demonstrated in conjunction with the electrogenerated chemiluminescent (ECL) detection of the target DNA. Compared to normal amplification, dendritic amplification allowed a 5-fold enhancement of the ECL signals. The higher sensitivity allowed by the dendritic amplification route was attributed to the hybridization between the DNA (Probe2DNA) on Probe1,2RSNP (normal amplification) and the complementary DNA (Probe2c DNA) on the additional Probe2cRSNP. As low as 1 fM of 22-bp-long target DNA was clearly detected. The experimental results demonstrated that the ECL intensity achieved through dendritic amplification showed a good linear relationship with the concentration of the target DNA over a wide linear range (10 fM∼10 pM).
Download: 5_Analyst.pdf
 6. Electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of a...
6. Electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of a...
 4. Highly sensitive gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric sens...
4. Highly sensitive gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric sens...






