Sungyool Bong, Sunghyun Uhm, Yang-Rae Kim, Jaeyoung Lee*, Hasuck Kim*
Electrocatalysis 2010, 1(2-3), 139−143
Publication online: July 20, 2010
Publication date: September 1, 2010
DOI: 10.1007/s12678-010-0021-2
ISSN: 1868-2529
Journal country: United States
Publisher: SPRINGER
URL: http://www.springerlink.com/content/h514r09567rr2617/
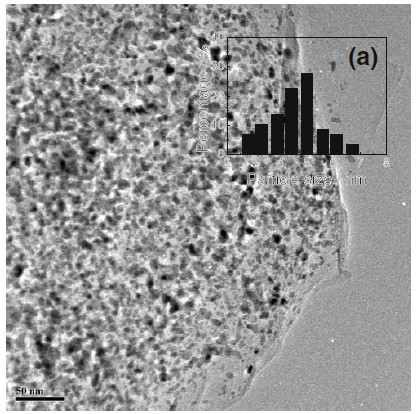
Abstract: Highly loaded 80 wt.% Pd/graphene nanosheet (GNS) electrocatalysts were synthesized by colloidal method in order to alleviate the degradation rate of Pd catalysts in formic acid oxidation. Pd nanoparticles deposited on the GNS were well distributed on the surface more homogenously and average particle size of these metals is 4.6 ± 0.6 nm as compared to Pd/VC (5.0 ± 1 nm), which is verified by X-ray diffraction peak and high-resolution transmission electron microscope images. Electrochemical measurements conducted by cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry show that Pd/GNS catalysts exhibited significantly enhanced electrocatalytic activity and stability for formic acid oxidation compared to Pd/VC catalysts.
Download: 9_Electrocatalysis.pdf

 10. Electrochemically programmed chemodosimeter on ultrathin ...
10. Electrochemically programmed chemodosimeter on ultrathin ...
 8. Chiral gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical sensor for ...
8. Chiral gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical sensor for ...











